Water Softeners DFW Metro Homeowners Can Count On
Is hard water plaguing your home, causing you to experience dry skin or build-up on your fixtures? Thanks to our residential water softeners, you can boost the quality of your home supply. These systems use an ion exchange process that lowers the concentration of dissolved minerals.
Components such as calcium and magnesium are absorbed within specialized resin beads. The softening process reduces the number of hard minerals within your water supply. As a result, you’ll avoid some of the inconveniences that hard water brings to your home!
Reliable Whole Home Water Filtration Systems
The water filtration process may sound simple, but it’s more complicated than one may think! With the help of our trustworthy technicians, you can expect a safe drinking supply within your DFW home. We aim to provide installation services that exceed your expectations, so you can hydrate without worry!
There are a variety of methods that are commonly used for water filtration. Many homeowners utilize sediment, activated charcoal or other filters for their residential supply. However, one method that has grown in popularity is reverse osmosis systems.
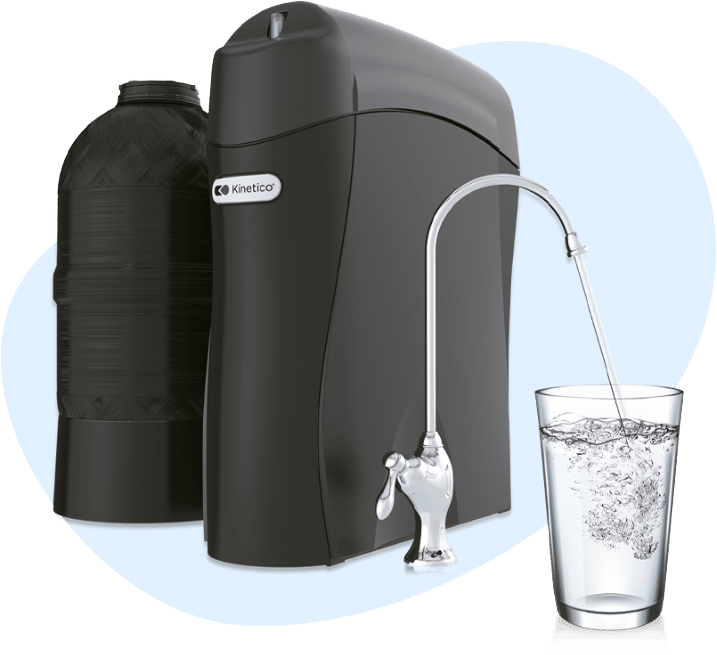
Whole House Reverse Osmosis Systems
If you’re looking for a filtration method that improves the taste and smell of your water, look no further than reverse osmosis technology! These systems filter water using a semi-permeable membrane. This tight-fitting layer prevents numerous microscopic particles from passing through, reducing impurities in your home supply.
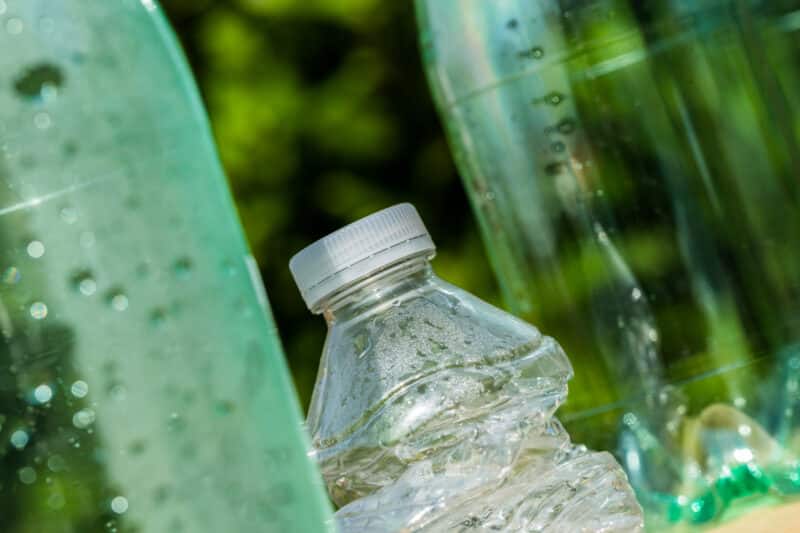
RO systems have advantages that go beyond clean water. This technology is highly versatile and efficient, catering to many uses and needs. Reverse osmosis filtration also benefits the environment. The average American uses roughly 150 water bottles per year, most of which are placed in landfills. With an RO system, you can reduce your plastic use and help the environment at the turn of a faucet handle.
Achieve Cleaner, Safer Water For Your Business
At Shelton’s Water, we understand the importance of having clean water in your place of business! Not only can it affect the health of your team, but it may affect whether or not you can legally operate.
Our team offers a variety of commercial water treatment services to help you obtain a healthy supply in your workspace. You can rest assured your water supply is in qualified hands.
Commercial Water Softener Installation
Hard water can be a pain for business owners to deal with. This substance is a hassle in households. However, it can also be a costly risk for commercial establishments. It can produce limescale within pipes. When this chalky matter builds up, it can reduce your plumbing system’s water pressure.
Additionally, the hardness levels can negatively impact the lifespan of any appliance that uses water to function. In time, this may add a few costly repairs to your plate. Installing a water softener in your workspace can reduce these risks, keeping your system in excellent condition.
Commercial Water Filtration Systems
No business owner wants to deal with water-related issues in their workspace. Almost every industry requires clean water to successfully operate! When you invest in a water filtration system for your commercial space, you can expect a clean supply that keeps the health of your employees and clientele in mind.
If you’re considering investing in a commercial RO system, Shelton’s Water offers free estimates on installation services! This technology provides guaranteed benefits for your workplace. You can say goodbye to metallic-tasting or cloudy tap water — expect a long-lasting solution for your business!
If It Has To Do With Water, Get Shelton’s Involved!
Shelton’s Water is proud to serve the residents in the Dallas Fort Worth Metroplex, including the surrounding areas! We keep health and cleanliness in mind, especially concerning your drinking water. If you have a residential or commercial need, you can count on our team to help with all your filtration essentials.
When it comes to your water, don’t settle for anything less than perfection. With years of experience under our belt, we’re prepared to aid your water quality. Our technology is top-of-the-line and will keep your supply in the best condition possible. Contact us today to explore our services and find the right solution for you!